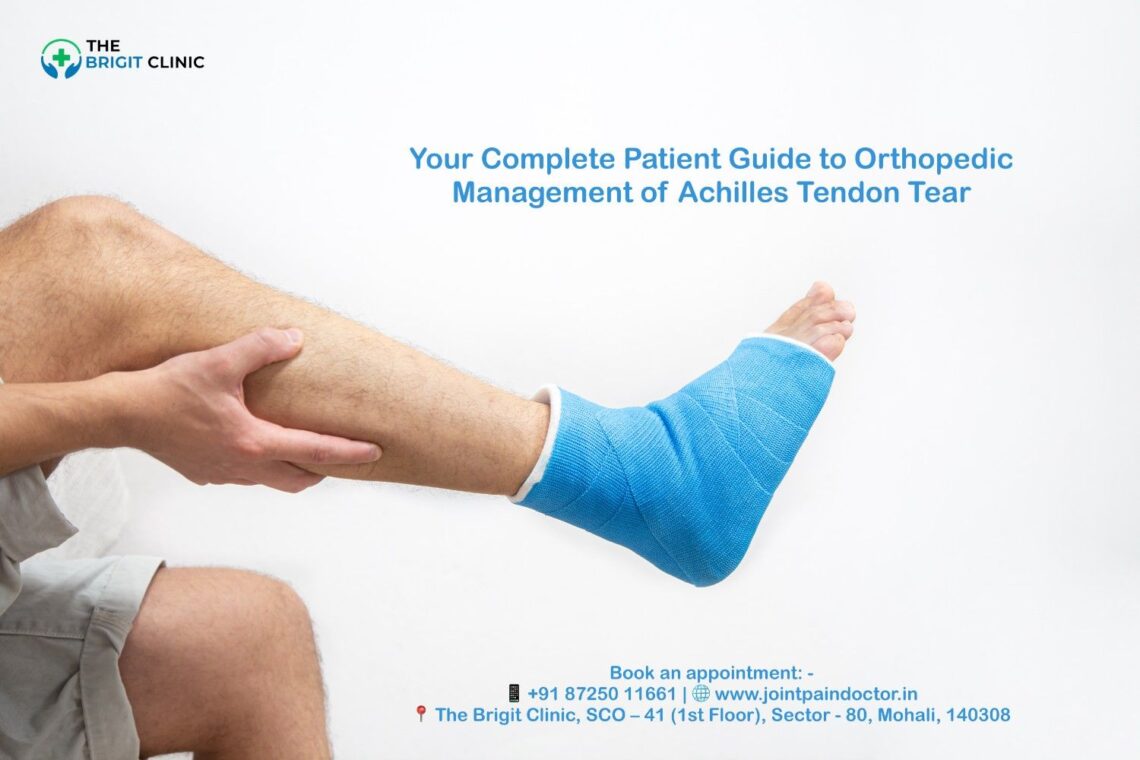
Despite being the largest tendon in your body and capable of withstanding forces up to 10 times your body weight, the Achilles tendon is surprisingly vulnerable to complications. Understanding the Orthopedic Management of Achilles Tendon Tear is the first step toward a successful recovery. Achilles tendon ruptures are very common sports injuries, occurring most frequently in people ages 30 to 40 and affecting men more often than women.
If you’re among the “weekend warriors” who exercise intensely without regular training, you face a higher risk of tearing your Achilles than younger, well-trained athletes. Additionally, these injuries can be missed in up to 25% of cases, making proper diagnosis crucial. Whether you’re dealing with a partial or complete tear, understanding your treatment options is essential for recovery. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about Achilles tendon tears—from identifying symptoms and risk factors to exploring both conservative and surgical treatment approaches that can help you return to your normal activities.
For expert diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan,
Consult the Best Orthopedic Doctor in Mohali or call +91 87250 11661
Understanding Achilles Tendon Tear
The Achilles tendon is a critical structure that plays a significant role in your daily movements. Understanding its function and how it can tear will help you better recognise and manage this injury.
What is the Achilles tendon?
The Achilles tendon, also called the calcaneal tendon, is the thickest and strongest tendon in your body. This fibrous band of tissue connects your calf muscles (gastrocnemius and soleus) to your heel bone (calcaneus). Located at the back of your lower leg, this powerful tendon spans approximately 6 to 10 inches in adults.
What makes the Achilles tendon remarkable is its incredible strength—it can support forces up to four times your body weight. This impressive capacity allows you to perform essential movements like walking, running, and jumping. When your calf muscles contract, they pull on the Achilles tendon, causing your foot to point downward (plantarflexion), which helps lift your heel off the ground during physical activities.
Partial vs complete Achilles tendon tear
Achilles tendon tears exist on a spectrum from minor damage to complete rupture. Understanding the difference between partial and complete tears is crucial for proper treatment.
In a partial tear, only a portion of the tendon fibres is damaged. Think of this like a frayed rope where some strands remain intact while others are torn. With a partial tear, you’ll experience:
- Localised soreness around the tendon
- Some swelling that gradually decreases
- Full function of the ankle despite pain
A complete tear occurs when the tendon ruptures entirely, separating into two distinct parts. This severe injury results in:
- A noticeable “pop” or snapping sound at the moment of injury
- Complete loss of strength and function in the ankle
- Extreme difficulty walking or exercising
- Significant swelling around the ankle
- In some cases, visible displacement of calf muscles
The Thompson test is commonly used by doctors to diagnose a complete rupture—when squeezing the calf fails to produce normal foot movement, it indicates a tear.
Common causes and overuse injuries
Most Achilles tendon tears happen during recreational sports or athletic activities. The tendon typically ruptures when exposed to sudden, powerful forces, especially during activities requiring quick stops, starts, and pivots—such as soccer, football, basketball, tennis, or squash.
Several specific scenarios commonly lead to tears:
- Landing awkwardly from a jump
- Cutting movements during sports
- Sudden acceleration or forceful pushing off with the foot
- Direct trauma to the tendon
- Tripping or falling, particularly when the foot is forced upward[18]
Certain factors increase your risk of experiencing an Achilles tendon tear. As you age, the tendon naturally becomes stiffer and weaker. “Weekend warriors”—adults who exercise intensely without regular training—face a higher risk than consistently trained athletes.
Furthermore, medical conditions like inflammatory diseases, diabetes, obesity, and certain medications (including fluoroquinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids) can weaken the tendon structure. Mechanical issues such as tight calf muscles, improper footwear, and training errors also contribute to vulnerability.
Overall, Achilles tendon ruptures affect approximately 12 per 100,000 individuals, most commonly occurring between ages 40 and 50, with men experiencing them 2 to 12 times more frequently than women.
If you're active and experiencing heel pain, visit a Sports Injury Clinic Mohali for a risk evaluation. Book your appointment or call +91 87250 11661
Recognising Symptoms and Risk Factors
Recognising an Achilles tendon tear promptly can make a significant difference in your treatment outcomes. By understanding the tell-tale signs and knowing your risk profile, you might prevent a delayed diagnosis that occurs in up to 25% of cases.
Sudden pop in the back of the ankle
The most distinctive sign of an Achilles tendon rupture is experiencing (and sometimes hearing) a sudden “pop” or “snap” at the back of your ankle. This sensation is so pronounced that many mistake it for being struck from behind. The sound represents the actual moment when your tendon fibres separate.
After this characteristic pop, you’ll likely feel immediate, intense pain. The sensation resembles what would happen if someone kicked you forcefully in the lower leg. Unlike gradual onset injuries, this moment is unmistakable and marks a clear point when damage occurred.
Call your doctor immediately if you experience this sudden snap during physical activity. This symptom alone strongly suggests a complete tear rather than a minor strain, consequently requiring proper medical evaluation.
Heel pain & swelling
Following a tear, sharp, sudden pain typically develops near your heel. Initially, this pain might be unbearable, though it sometimes subsides slightly after the acute injury. The area around your Achilles tendon will swell noticeably, often accompanied by bruising along the back of the ankle.
The discomfort pattern differs from other foot conditions. With an Achilles tendon tear, pain tends to be localised specifically to the back of the ankle where the tendon attaches to your heel bone. Throughout the day, this pain might intensify with activity.
Morning stiffness presents another common symptom, where the affected area feels particularly tight and sore when you first get up. As you move around, this stiffness sometimes improves temporarily.
Calf pain after injury
Beyond the immediate heel area, pain often radiates upward into your calf muscle. This happens because the calf muscles connect directly to the Achilles tendon, creating a continuous pain pathway.
The discomfort in your calf typically worsens during activities that engage these muscles, such as climbing stairs or walking uphill. Furthermore, weakness in the leg becomes apparent when attempting to push off with the affected foot.
For partial tears, you might maintain some function despite the pain. However, with complete ruptures, standing on tiptoes or performing basic foot movements becomes nearly impossible.
Risk factors for Achilles tendon tear
Several factors increase your vulnerability to Achilles tendon tears:
Age and Gender: The peak age for ruptures occurs between 30-40 years, though some sources identify 40-50 as the highest risk period. Men experience these injuries four to five times more frequently than women.
Activity Patterns: “Weekend warriors” face significantly higher risk than regularly trained athletes. Sports involving quick stops, starts, and pivots present the greatest danger—particularly soccer, basketball, tennis, football, and racquet games.
Medical Factors: Certain conditions predispose you to tendon injuries:
- Previous Achilles tendinopathy
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol or blood pressure
- Psoriasis
- End-stage kidney disease
- Inflammatory arthritis
Medication Usage: Some medications weaken tendon structure, notably:
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics[28]
- Corticosteroid injections
- Oral bisphosphonates
Biomechanical Issues: Physical characteristics matter too. Having tight calf muscles, flat arches, overpronation (ankles rolling inward), or legs of different lengths all increase your risk[30].
Understanding these symptoms and risk factors helps you identify potential problems early and seek appropriate orthopaedic management for Achilles tendon tears before complications develop.
Experienced a pop or snap in your ankle? Seek immediate consultation with an Orthopedic Doctor in Mohali for Achilles Tear, call +91 87250 11661
How Achilles Tendon Tears Are Diagnosed
Getting an accurate diagnosis is essential for proper orthopaedic management of an Achilles tendon tear. Medical professionals use several examination techniques combined with imaging to confirm your injury.
Physical exam and Thompson test
Your doctor will begin by asking about your symptoms and medical history, followed by a thorough physical examination of your lower leg. During this examination, they’ll check for tenderness, swelling, and potentially feel for a gap in your tendon if it has ruptured completely.
The Thompson test (sometimes called the calf squeeze test) is a key diagnostic procedure with 96-100% sensitivity and 93-100% specificity for detecting Achilles ruptures. Here’s how it works:
- You’ll lie face down with your feet hanging over the edge of the exam table
- Your doctor will gently squeeze your calf muscle
- In a healthy tendon, this causes your foot to point downward naturally
- If your foot doesn’t move during the squeeze, it indicates a likely rupture
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors often use additional clinical signs like checking for a palpable gap in the tendon (typically 3-6cm above the heel) and assessing plantar flexion strength.
MRI vs Ultrasound in Achilles tendon tear
Both MRI and ultrasound provide valuable diagnostic information, albeit with different strengths:
Ultrasound shows the tendon in real-time and demonstrates how it responds to movement. It’s highly accurate with 95% sensitivity and 99% specificity for detecting full-thickness tears. Ultrasound is generally:
- More cost-effective
- Readily available
- Excellent for detecting tendinopathy and complete ruptures
MRI creates detailed images of soft tissues and is particularly valuable for:
- Detecting partial tears (superior to ultrasound)
- Assessing the distance between torn tendon ends
- Postoperative evaluation
- Ruling out other injuries with similar symptoms
Most specialists recommend ultrasound over MRI for initial diagnosis and monitoring, though your doctor may order both depending on your specific situation.
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- A popping or snapping sound at the time of injury
- Suddenly, severe pain in the back of your ankle
- Difficulty walking or standing on tiptoes
- Visible swelling around the heel area
Even if you can walk with a ruptured Achilles (which many people can), it’s crucial to see a healthcare provider promptly. Using your ankle and putting full weight on it before diagnosis can worsen the injury. Importantly, up to 20% of Achilles tendon ruptures are initially misdiagnosed, often confused with ankle sprains, making proper medical evaluation essential for effective treatment.
For advanced diagnostic imaging and expert interpretation, visit the Best Ortho Doctor in Mohali. Schedule your visit.
Treatment Options: Conservative and Surgical
Treatment decisions for Achilles tendon tears depend on several factors, including your age, activity level, and the severity of your injury. Both non-surgical and surgical approaches offer viable pathways to recovery, each with distinct advantages.
Achilles tendon tear – conservative management
Conservative treatment involves non-surgical approaches that typically include rest, immobilisation, and controlled rehabilitation. This option is often suitable for older patients, those with limited activity goals, or individuals with health conditions that increase surgical risks.
For partial tears with less than 5mm gap between ruptured tendon edges, conservative management can be particularly effective. The traditional approach involves wearing a below-knee cast in an equinus (pointed down) position for four weeks without weight-bearing, followed by a neutral position cast with weight-bearing for another four weeks.
Surgical treatment of Achilles tendon tear
Surgical intervention appears to be the preferred method for athletes and younger, active individuals. The primary benefit of surgery is a lower re-rupture rate compared to non-surgical treatment.
The procedure typically involves making an incision in the back of your leg and stitching the torn tendon together. In cases of severe degeneration, surgeons may remove damaged portions and repair the remaining healthy tendon.
Minimally invasive Achilles tendon tear surgery
This advanced technique involves a small 3-4cm incision instead of the traditional 10cm cut. Through this smaller opening, specialised instruments guide sutures into the tendon to complete the repair.
The minimally invasive approach offers several advantages:
- Reduced wound healing issues
- Lower infection rates
- Less scar tissue formation
- Faster return to normal activities
Immobilisation vs early mobilisation in Achilles tendon tear
Historically, rigid cast immobilisation for six weeks was standard practice. Nevertheless, recent research strongly supports early functional rehabilitation and mobilisation.
Studies demonstrate that early mobilisation doesn’t increase re-rupture rates. Moreover, it offers superior benefits:
- Decreases excessive adhesion formation
- Improves the biomechanical properties of healing tissue
- Enhances tendon gliding function
- Reduces joint stiffness and muscle atrophy
Medication for tendon inflammation
Pain management typically begins with over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium. For persistent discomfort, prescription medications might include COX-2 inhibitors, which potentially cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects than traditional NSAIDs.
PRP Achilles tendon tear therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of your own platelets into the injured area. These platelets contain growth factors that may promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Currently, evidence regarding PRP effectiveness remains mixed. Some studies show improvements in ankle dorsiflexion angle and calf circumference, whereas others found no significant differences in patient-reported outcomes at two years post-injury.
Explore all treatment options, including Minimally Invasive Achilles Surgery in Mohali, with the Best Orthopedician in Mohali. Discuss your choices at https://jointpaindoctor.in/ or
Call *+91 87250 11661* to learn more about the Achilles Tear Surgery Cost Mohali.
Recovery, Rehab, and Return to Activity
Full healing from an Achilles tendon tear requires a comprehensive rehabilitation approach tailored to your specific needs. The recovery journey typically spans four to six months, regardless of whether you underwent surgical or non-surgical treatment.
Physical therapy and strengthening
Physical therapy serves as the cornerstone of Achilles tendon rehabilitation. The duration varies based on injury severity—from a few weeks to several months. Your therapist will focus on three primary goals: pain relief through various modalities, restoring proper movement patterns, and rebuilding muscle strength and balance.
Eccentric exercises stand out as the most evidence-based intervention for Achilles rehabilitation. This approach, typically performed twice daily for at least 11 weeks, has been shown to reduce pain by an average of 60% across multiple clinical trials. The Alfredson protocol remains the gold standard, gradually progressing from bilateral to single-leg heel raises.
For optimal recovery, maintain a consistent exercise regimen alongside gradually increasing weight-bearing activities. Initially, you’ll use a walking boot with progressively decreasing heel wedges until reaching a neutral position, usually around 6-8 weeks post-injury.
Custom orthotics post Achilles repair
Bespoke orthotics play a valuable role in recovery by providing proper foot alignment, enhancing shock absorption, and correcting biomechanical issues that might stress your healing Achilles tendon. These devices primarily keep your heel raised, reducing the workload on the tendon while protecting against re-rupture.
Studies have demonstrated that custom foot orthoses can significantly improve symptoms in athletes with Achilles tendinopathy, with participants reporting an average 92% improvement when using high-density EVA orthotics.
Equinus contracture after Achilles tendon tear
Equinus contracture—excessive tightness limiting ankle dorsiflexion—often develops following Achilles injuries. Conservative management through physical therapy, stretching, and night splints should be attempted first. For refractory cases, surgical options include gastrocnemius lengthening, soleus fascial release, or Achilles tendon lengthening procedures.
Return to sports after Achilles tendon tear
Returning to sports requires patience—full athletic activities should be avoided for at least 6 months post-injury. The return process follows a carefully structured progression: controlled strengthening, followed by plyometric training, and finally sport-specific movements.
Before resuming competitive activities, you should achieve specific milestones: single-leg heel raise at 90% height compared to your uninjured side, normal gait mechanics, and pain-free performance of sport-specific movements. Even with optimal rehabilitation, expect some persistent strength deficits (10-30%) in the affected leg beyond the one-year mark.
Access comprehensive rehabilitation programs at our Orthopedic Hospital in Mohali for the Achilles Rupture facility. Start your recovery journey with the Best Achilles Tendon Surgeon in Mohali by calling +91 87250 11661
Conclusion
Achilles tendon tears represent serious injuries that require prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment for optimal recovery. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how these tears happen, their symptoms, and the available treatment approaches. Whether you choose conservative management or surgical intervention, your recovery journey demands patience and commitment to rehabilitation protocols.
Most patients can expect a full recovery period of four to six months, though some strength deficits might persist beyond the one-year mark. During this time, physical therapy will become your essential ally, particularly through eccentric strengthening exercises that have proven highly effective for tendon healing.
Remember that each case differs based on factors like age, activity level, and tear severity. Therefore, working closely with healthcare professionals remains crucial for developing a personalised treatment plan. Custom orthotics might benefit your recovery by improving foot alignment and reducing stress on your healing tendon.
Though returning to sports and normal activities takes time, a structured approach to rehabilitation significantly improves your outcomes. Above all, don’t rush this process. Your body needs adequate time to rebuild the strongest tendon in your body.
Armed with this knowledge about Achilles tendon tears, you can now make informed decisions about your care if faced with this injury. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt medical attention, and dedication to your rehabilitation program will ultimately determine your successful return to the activities you enjoy.
For a successful recovery under expert guidance, book your final consultation at https://jointpaindoctor.in/ or call +91 87250 11661
Key Takeaways
Understanding Achilles tendon tears and their proper management can significantly impact your recovery outcomes and help you make informed treatment decisions.
• Recognise the warning signs early: A sudden “pop” sound, severe heel pain, and inability to stand on tiptoes indicate a potential Achilles rupture requiring immediate medical attention.
• Both surgical and conservative treatments work: Your age, activity level, and tear severity determine the best approach—athletes often benefit from surgery while older patients may succeed with non-surgical management.
• Early mobilisation beats prolonged immobilisation: Modern rehabilitation emphasises controlled movement over extended casting, leading to better outcomes and faster functional recovery.
• Recovery takes 4-6 months minimum: Patience is crucial as rushing back to activities increases re-rupture risk—expect some strength deficits even after one year.
• Physical therapy is non-negotiable: Eccentric strengthening exercises, particularly the Alfredson protocol, form the foundation of successful rehabilitation regardless of treatment method chosen.
The key to successful Achilles tendon recovery lies in prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, and unwavering commitment to structured rehabilitation. Don’t underestimate this injury—proper management now prevents long-term complications and ensures your return to normal activities.
Ready to start your treatment? Contact the Best Orthopedic Doctor Mohali today
or call +91 87250 11661
FAQs
Q1. What are the main symptoms of an Achilles tendon tear?
A1. The primary symptoms include a sudden “pop” or snapping sensation in the back of the ankle, intense heel pain, swelling around the affected area, and difficulty walking or standing on tiptoes.
Q2. How long does it typically take to recover from an Achilles tendon tear?
A2. Recovery usually takes 4-6 months, regardless of whether surgical or non-surgical treatment is chosen. However, some strength deficits may persist for over a year.
Q3. Is surgery always necessary for an Achilles tendon tear?
A3. Not always. The decision between surgical and conservative treatment depends on factors like age, activity level, and tear severity. Athletes often benefit from surgery, while older patients may succeed with non-surgical management.
Q4. What role does physical therapy play in Achilles tendon tear recovery?
A4. Physical therapy is crucial for recovery, focusing on pain relief, restoring proper movement, and rebuilding strength. Eccentric exercises, particularly the Alfredson protocol, are considered highly effective for rehabilitation.
Q5. When can I return to sports after an Achilles tendon tear?
A5. Full athletic activities should be avoided for at least 6 months post-injury. Before returning to competitive sports, you should achieve specific milestones like single-leg heel raises at 90% height compared to the uninjured side and pain-free performance of sport-specific movements.
About the Doctor – Dr. Manu Mengi
Dr. Manu Mengi is a highly skilled and renowned Orthopedic Surgeon in Mohali, specialising in the management and treatment of sports injuries, particularly complex Achilles tendon tears. With extensive experience and a commitment to adopting the latest surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures, Dr. Mengi provides personalised care to each patient. He leads a state-of-the-art Ortho Clinic in Mohali that is equipped with advanced diagnostic technology to ensure accurate assessments and the most effective treatment plans. Dedicated to helping patients return to their active lifestyles, Dr. Mengi is considered one of the best orthopedic doctors in the region for Achilles tendon repair and rehabilitation.
Book an Appointment today -
📱 +91 87250 11661 | 🌐 Read Reviews | 📍 Get Directions