Ankylosing spondylitis affects approximately 1.7 million adults in the United States, with a prevalence rate of 0.2-0.5% of the population. Unlike common backaches that come in short, painful spells, the pain from this chronic inflammatory condition is typically long-lasting and can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Most people develop ankylosing spondylitis during their late teens or early twenties, with about 80% of patients experiencing symptoms before age 30.
When examining genetic factors, more than 95% of Caucasian individuals with ankylosing spondylitis carry the HLA-B27 gene. The condition also shows a gender disparity, occurring twice as frequently in men as in women. While there’s no cure for ankylosing spondylitis, early detection and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and potentially slow disease progression. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything from diagnosis methods like HLA-B27 testing and x-ray findings to various management strategies, including medications, physical therapy, and surgical options for those with advanced spinal changes.
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) belongs to a family of inflammatory diseases known as spondyloarthritis, which primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. This condition is characterised by its autoimmune nature – essentially, your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body instead of protecting it.
What is autoimmune arthritis of the spine?
Ankylosing spondylitis is fundamentally an inflammatory disease of the axial skeleton. Unlike typical wear-and-tear arthritis, AS is driven by chronic inflammation that can eventually lead to new bone formation and fusion of vertebrae. Although experts haven’t pinpointed the exact cause, genetic factors play a crucial role – specifically, mutations in genes like human leukocyte antigen-B (HLA-B27). Research shows that over 90% of white individuals with AS carry this mutated gene.
The condition is generally considered more autoinflammatory than autoimmune, with the innate immune system playing a central role in its development. However, emerging research suggests AS might actually represent a combination of both autoinflammatory and autoimmune processes.
How AS affects the sacroiliac joints and spine
AS typically begins with inflammation in the sacroiliac joints, where your spine connects to your pelvis. These large joints are used whenever you move or shift your hips. The inflammation causes pain and stiffness, particularly noticeable in the lower back. As the disease progresses, this inflammation can spread upward along the spine.
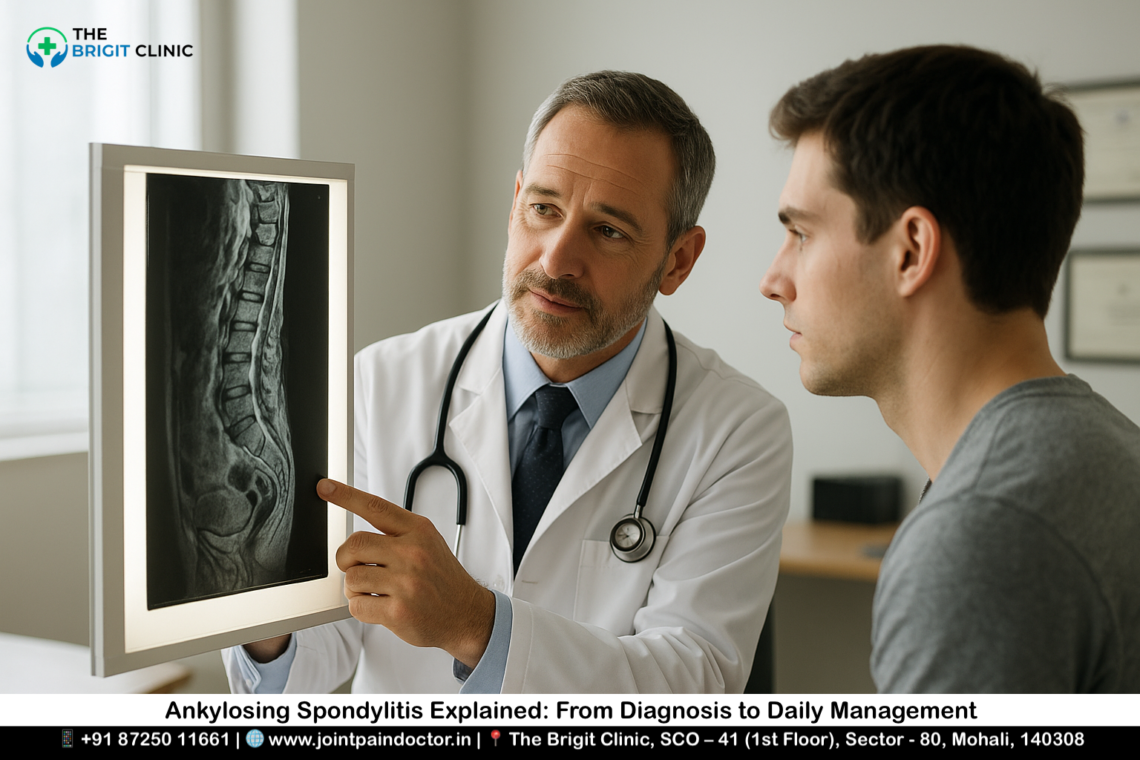
Eventually, in severe cases, the ongoing inflammation triggers the body’s healing response, leading to new bone formation. This process can cause vertebrae to fuse, creating the characteristic “bamboo spine” appearance visible on X-rays. This fusion reduces spine flexibility and may result in a hunched posture.
Beyond the spine, AS can affect other joints such as the shoulders, hips, and knees. Moreover, approximately 25-35% of individuals develop acute anterior uveitis (eye inflammation), and up to 50% experience inflammatory bowel disease.
Difference between AS and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
AS and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) represent two ends of the same disease spectrum. The key distinction lies in imaging results – particularly X-rays of the sacroiliac joints.
In AS (also called radiographic axial spondyloarthritis), damage to the sacroiliac joints is clearly visible on X-rays. Conversely, nr-axSpA patients show similar symptoms but without definitive X-ray evidence of sacroiliitis. Nevertheless, MRI technology might reveal active inflammation in nr-axSpA patients even before changes appear on X-rays.
Interestingly, these subtypes show demographic differences. AS affects males more frequently (about 70.4% of cases), whereas nr-axSpA shows a more balanced gender distribution (males account for approximately 46.5%). Furthermore, HLA-B27 prevalence is lower in nr-axSpA patients (54.3%) compared to AS patients (92.7%).
Is your back pain inflammatory? Don't ignore persistent stiffness. Consult with an experienced Back Pain Doctor in Mohali at The Brigit Clinic for an accurate diagnosis. Book Your Appointment Today!
Recognising the Symptoms Early
Early detection of ankylosing spondylitis starts with recognising its distinctive symptoms. The signs often develop gradually over months or years and may fluctuate in intensity.
Inflammatory back pain symptoms to watch for
The hallmark of ankylosing spondylitis is inflammatory back pain, which differs significantly from mechanical back pain. Pain typically begins in early adulthood before age 40 and develops gradually rather than suddenly. Initially, symptoms might come and go for weeks or months at a time.
What makes this pain unique:
- Worsens after prolonged rest or sitting
- Improves with physical activity
- Often most severe in the early morning or during the night
- Frequently causes stiffness lasting more than an hour after waking
Notably, this pattern reverses what we see in typical back pain, where rest usually provides relief and activity worsens symptoms.
Sacroiliac joint inflammation and stiffness
Sacroiliitis—inflammation of the sacroiliac joints where your spine connects to your pelvis—is frequently the first sign of ankylosing spondylitis. This inflammation causes pain in the lower back and buttock areas that can radiate to the hips, thighs, and sometimes legs.
The pain from sacroiliitis may feel suddenly sharp and stabbing or present as a constant dull ache. Many patients report pain that worsens when turning or rotating their hips. This discomfort can significantly affect daily activities, especially sitting for extended periods.
Fatigue, eye inflammation, and other systemic signs
Beyond joint symptoms, ankylosing spondylitis often affects multiple body systems. Extreme fatigue affects many patients regardless of how much they rest. Additionally, about 25-35% of individuals develop uveitis—inflammation of the eye’s iris—causing redness, pain, blurred vision, and light sensitivity.
Other systemic manifestations may include:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (affecting up to 50% of individuals)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Skin rashes
- Shortness of breath
Progressive spinal fusion and posture changes
If left untreated, ongoing inflammation triggers the body’s healing response, leading to new bone formation between vertebrae. This process, called spinal fusion, creates the characteristic “bamboo spine” appearance visible on X-rays.
As the disease advances, postural changes become increasingly apparent. The spine may develop increased kyphosis (forward curve), with compensatory changes in the lower body. The progressive fusion limits mobility and can eventually restrict chest expansion, affecting breathing capacity.
Experiencing morning back stiffness or unexplained fatigue? Early intervention is key. Visit the leading Ortho Clinic in Mohali for a comprehensive evaluation. Call us at +91 87250 11661.
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis often presents significant challenges, as the condition develops slowly with no definitive single test to confirm its presence.
Early detection of ankylosing spondylitis
Obtaining an early diagnosis typically requires a combination of clinical assessment, imaging, and laboratory tests. The modified New York Criteria remains the most commonly used diagnostic framework, requiring both clinical symptoms and radiographic evidence of sacroiliitis. Consequently, many patients experience a delay of 7-10 years between symptom onset and formal diagnosis.
Role of HLA-B27 testing in diagnosis
While approximately 90-95% of ankylosing spondylitis patients test positive for HLA-B27, this genetic marker alone cannot confirm diagnosis. Indeed, only 1-5% of people carrying this gene variant actually develop the condition. The test primarily serves as a supporting factor in diagnosing suspected cases, given that 7.5% of white Americans carry HLA-B27 without developing symptoms.
X-ray findings and radiographic changes
X-rays represent the traditional gold standard for assessing structural changes in ankylosing spondylitis. Key radiographic findings include bilateral sacroiliitis, vertebral “squaring,” syndesmophytes (vertical bony outgrowths), and in advanced cases, the characteristic “bamboo spine” appearance. For reliable assessment of spinal progression, an observation period of at least 2 years is recommended.
MRI and blood tests for inflammation markers
MRI has revolutionised early diagnosis by detecting inflammatory changes before they become visible on X-rays. Blood tests for inflammation—including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP)—often show elevated levels, though these markers may be normal in up to half of patients. Unlike other inflammatory arthritis conditions, ankylosing spondylitis patients sometimes show minimal blood inflammation despite significant symptoms.
Confused by your symptoms and test results? Get a clear diagnosis and personalised treatment plan from theBack Pain Specialist in Mohali.
Visit Our Google My Business Page to See Patient Reviews
Treatment and Management Options
Treatment options for ankylosing spondylitis have expanded tremendously, offering hope for symptom management and disease control. While there’s no cure, proper treatment can help most patients lead active lives.
NSAIDs for ankylosing spondylitis pain relief
NSAIDs remain the cornerstone first-line treatment for AS. These medications effectively reduce inflammation and pain while improving function. Studies show all NSAIDs significantly outperform placebo in reducing pain severity. Etoricoxib ranks as the most effective NSAID for AS patients. However, these medications carry risks – particularly gastrointestinal issues with diclofenac and naproxen showing significantly higher rates of GI events compared to placebo.
DMARDs and biologics: slowing disease progression
For patients who don’t respond adequately to NSAIDs, disease-modifying treatments offer hope. TNF inhibitors dramatically improve symptoms by blocking the TNF cytokine, a key inflammation driver. Long-term TNF inhibitor use may reduce radiographic progression in AS patients.
Newer biologics include IL-17 inhibitors (secukinumab, ixekizumab, bimekizumab), which effectively target another inflammatory pathway. JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib and upadacitinib, taken orally rather than by injection, represent the latest treatment advance.
Corticosteroid injection for flare-ups
Corticosteroid injections can temporarily relieve inflammation in specific joints. Pain relief typically lasts several months. Side effects may include short-term pain flares, facial flushing, and blood sugar increases. Doctors typically limit injections to three times yearly in the same joint, with at least three months between treatments.
Physical therapy and orthopaedic bracing
Physical therapy stands as a crucial element in AS management. Regular exercises help reduce stiffness, improve posture, decrease pain, strengthen muscles, and enhance flexibility. Physical therapists can design personalised programs incorporating core strengthening, flexibility exercises, and deep breathing techniques.
Orthopaedic bracing provides support and stability for affected joints. Properly fitted braces can reduce pain, improve stability, and enhance function.
Surgical options: hip replacement and spinal osteotomy
When conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary. Total hip arthroplasty effectively alleviates pain and improves function in AS patients with severe hip involvement. For significant spinal deformities, osteotomy procedures can correct posture and restore sagittal balance.
Disability reduction and prevention of joint fusion
The ultimate goal of all treatments is to prevent disability and joint fusion. Early intervention with appropriate medications, consistent physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications offers the best chance at maintaining function and quality of life.
Explore advanced Back Pain Treatment in Mohali tailored to your needs. From NSAIDs to modern therapies, find relief at The Brigit Clinic. Explore Your Treatment Options
Conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis presents unique challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Though no cure exists currently, early detection coupled with comprehensive treatment significantly improves quality of life. Understanding the distinctive symptoms—particularly inflammatory back pain that improves with activity rather than rest—helps identify this condition before irreversible damage occurs.
After diagnosis, many treatment options become available to manage symptoms effectively. NSAIDs generally serve as first-line therapy, while biologics and JAK inhibitors offer hope for those with inadequate response. Additionally, regular physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining spinal mobility and function throughout the disease course.
Living with ankylosing spondylitis certainly requires adjustments, but advances in treatment have transformed the outlook for most patients. The combination of medication, exercise, and lifestyle modifications allows many individuals to lead active, fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis. Most importantly, proactive management helps prevent the most severe complications like spinal fusion and significant disability.
For anyone experiencing persistent lower back pain with morning stiffness, seeking medical evaluation promptly might make all the difference. The journey from diagnosis to daily management may seem daunting at first, but with proper support and treatment, the path forward becomes much clearer. Remember that each person’s experience with ankylosing spondylitis differs, and finding the right treatment approach often requires patience and partnership with healthcare providers.
Key Takeaways
Understanding ankylosing spondylitis is crucial for early detection and effective management of this chronic inflammatory condition that affects millions worldwide.
• Early recognition saves mobility: Inflammatory back pain that worsens with rest but improves with activity signals AS, unlike typical back pain patterns.
• Genetic testing provides clues: Over 90% of AS patients carry the HLA-B27 gene, but only 1-5% of carriers develop the condition.
• Treatment prevents fusion: NSAIDs, biologics, and consistent physical therapy can slow disease progression and prevent irreversible spinal fusion.
• Exercise is medicine: Regular physical therapy and movement are essential for maintaining spinal flexibility and reducing long-term disability.
• Early diagnosis matters: Most patients wait 7-10 years for diagnosis, but prompt treatment significantly improves quality of life outcomes.
The key to successful AS management lies in recognising symptoms early, pursuing comprehensive treatment, and maintaining an active lifestyle. While there’s no cure, modern treatments allow most patients to lead fulfilling lives when properly managed.
FAQs
Q1. What are the early signs of ankylosing spondylitis?
A1. Early signs include persistent lower back pain that improves with activity, morning stiffness lasting over an hour, and pain in the sacroiliac joints. Some people may also experience fatigue, eye inflammation, and other systemic symptoms.
Q2. How is ankylosing spondylitis diagnosed?
A2. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical assessment, imaging tests (X-rays and MRI), and blood tests. Doctors look for inflammatory back pain symptoms, radiographic evidence of sacroiliitis, and may test for the HLA-B27 gene, which is present in most patients with AS.
Q3. What treatment options are available for ankylosing spondylitis?
A3. Treatment options include NSAIDs for pain relief, biologics like TNF inhibitors to slow disease progression, physical therapy to maintain mobility, and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery for severe joint damage.
Q4. Can ankylosing spondylitis be cured?
A4. There is no cure for ankylosing spondylitis, but early detection and appropriate treatment can effectively manage symptoms and potentially slow disease progression, allowing many patients to lead active lives.
Q5. How does ankylosing spondylitis differ from typical back pain?
A5. Unlike typical back pain that improves with rest, ankylosing spondylitis pain often worsens with inactivity and improves with exercise. Pain is also typically more persistent, accompanied by morning stiffness, and often starts before age 40.
Ready to take the next step towards managing your AS? Schedule a consultation with the Best Back Pain Doctor in Mohali, Dr. Manu Mengi. Call +91 87250 11661 or visit us at SCO – 41, Sector - 80, Mohali.
About Dr. Manu Mengi – Best Ortho Doctor in Mohali
Dr. Manu Mengi is a renowned and trusted name in orthopedics, dedicated to providing exceptional care for patients with complex joint and spine conditions like Ankylosing Spondylitis. With extensive experience and a patient-centric approach, he is committed to accurately diagnosing the root cause of pain and creating effective, personalised management plans. At The Brigit Clinic, one of the leading Orthopedic Clinics in Mohali, Dr. Mengi utilises the latest advancements in medical science to help patients reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance their quality of life. His expertise makes him the preferred choice for anyone seeking the Best Ortho Doctor in Mohali.
Book an Appointment today -
📱 +91 87250 11661 | 🌐 Read Reviews |📍 Get Directions