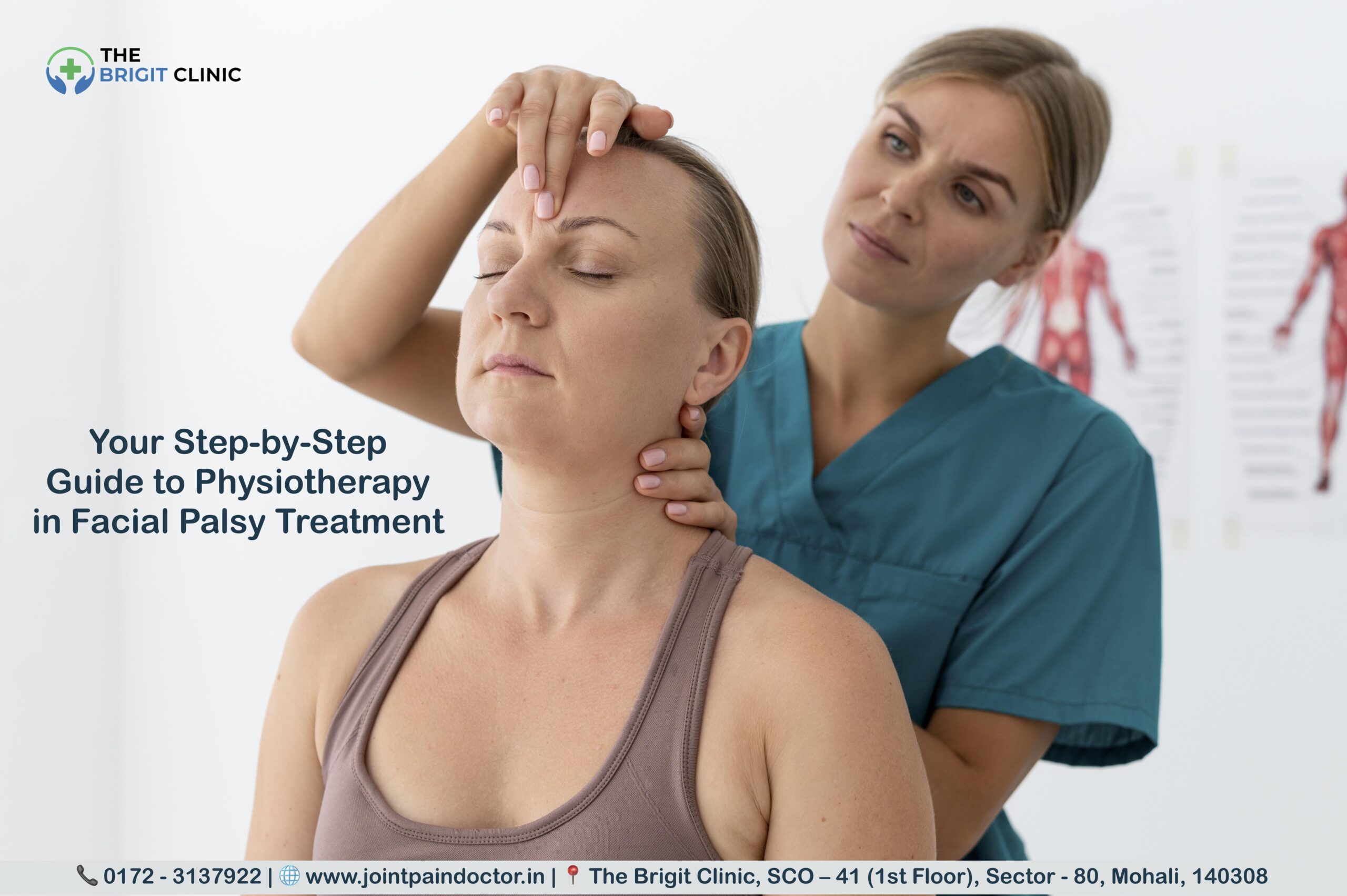
Bell’s palsy and other forms of facial nerve paralysis affect 11-40 people per 100,000 annually, with physiotherapy in facial palsy emerging as a crucial treatment approach. Unfortunately, one in three patients (29%) experiences poor recovery, resulting in permanent facial function deficits. This can lead to significant psychological distress, depression, and even social alienation as people withdraw from public-facing roles.
Fortunately, the evidence, though limited in size, strongly supports the use of facial palsy exercises and rehabilitation techniques to accelerate recovery and minimise adverse outcomes. In fact, approximately 70% of people with Bell’s palsy recover completely without treatment within 3-6 months, but with proper physiotherapy interventions, we can potentially improve outcomes for the remaining 30%. Additionally, research indicates that facial exercises may significantly improve facial function, especially when combined with other treatments.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about physiotherapy for facial nerve paralysis – from recognising symptoms to implementing advanced rehabilitation techniques for recovery of facial symmetry. Whether you’re dealing with post-stroke facial palsy or Bell’s palsy (which accounts for about 60-75% of all facial paralysis cases in the United States), this step-by-step approach will help you understand how neurological rehabilitation can restore both function and confidence.
Ready to begin your recovery journey? Trust your care to Mohali's Top Physiotherapist at The Brigit Clinic. We create personalised plans for optimal results. Schedule Your Assessment Today!
Step 1: Recognising the Signs of Facial Palsy
Facial palsy can appear suddenly or develop gradually, causing varying degrees of muscle weakness on one or both sides of the face. Recognising these symptoms early allows for prompt intervention, potentially improving long-term outcomes through timely physiotherapy and medical care.
Early symptoms to watch for
The onset of facial palsy symptoms can be quite dramatic – appearing overnight or developing over two to three days. In other cases, symptoms may emerge gradually over weeks or even months. Initially, you might notice:
- Drooping or flattening on one side of the face
- One-sided smile or difficulty making facial expressions
- Problems closing your eye completely on the affected side
- Facial droop affecting the brow, eye, cheek, and mouth
- Drooling due to reduced muscle control
- Pain around the jaw or behind the ear
- Increased sensitivity to sound
- Headache or slight fever
The severity can range from mild weakness to complete paralysis of facial muscles. Furthermore, some people experience numbness or heaviness in their face, yet can still feel touch and temperature sensations. Changes in tear production and saliva may also occur, along with potential taste loss.
For most people with Bell’s palsy (which accounts for many facial palsy cases), symptoms reach their maximum severity within 48-72 hours. During this period, you’ll likely notice the most pronounced facial asymmetry.
When to seek medical help
If you experience any sudden facial weakness or drooping, seek medical attention immediately. This is crucial because facial paralysis can sometimes indicate a serious condition like stroke, even though most cases turn out to be Bell’s palsy.
Call emergency services (911) immediately if facial weakness is accompanied by:
- Weakness or paralysis in arms or legs
- Difficulty walking or coordination issues
- Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- Blurred or double vision
- Suddenly, a severe headache
- Memory loss or confusion
Generally, even if facial weakness is your only symptom, you should visit your doctor as soon as possible for proper diagnosis. This is particularly important since early treatment with steroids (within 72 hours) improves outcomes for Bell’s palsy – 83% of treated patients achieve full recovery compared to only 72% of untreated patients.
Additionally, seek prompt medical evaluation if symptoms develop slowly over weeks or months, as this might indicate an underlying condition requiring specialised treatment. Similarly, contact your healthcare provider immediately if you notice painful vesicular rashes in or around your ear, mouth, or scalp, as this could indicate Ramsay Hunt Syndrome requiring antiviral medication.
Post-stroke facial palsy indicators
Central facial paralysis (CFP) affects approximately 45% of stroke patients. Unlike Bell’s palsy, post-stroke facial weakness typically affects only the lower part of the face – the area below the eye clefts. Moreover, you might observe:
- The ability to wrinkle your forehead and raise eyebrows remains intact
- Weakness primarily affects the mouth and cheek region
- Associated symptoms like dysphagia (swallowing difficulties) and dysarthria (speech problems)
- Increased muscle tension and decreased muscle strength
Post-stroke facial palsy often coincides with other stroke symptoms previously mentioned. Consequently, prompt medical care is essential as this represents a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to minimise brain damage.
Beyond physical symptoms, facial paralysis frequently causes psychological impacts. Patients with facial paralysis are more likely to experience anxiety and depression, which may subsequently affect motivation during rehabilitation. Therefore, recognising and addressing both physical and emotional aspects is vital for comprehensive recovery.
Noticed sudden facial drooping or weakness? Early intervention is critical. Contact the leading Physiotherapy Clinic in Mohali for prompt evaluation and care. Call us at 📞 0172 - 3137922.
Step 2: Getting a Proper Diagnosis
After noticing facial weakness symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective physiotherapy in facial palsy treatment. A proper diagnosis determines both the cause and severity of your condition, directly influencing your rehabilitation plan.
Initial clinical assessment
The diagnostic journey typically begins with a thorough clinical examination by a healthcare professional. Your doctor will visually examine your face to assess the extent of paralysis and muscle control. During this assessment, they’ll ask you to perform specific facial movements like smiling, blinking, raising your eyebrows, and closing your eyes.
The clinical evaluation critically distinguishes between central nervous system causes (stroke, brain tumour, multiple sclerosis) and peripheral causes (Bell’s palsy, ear infections, facial nerve tumours). One key differentiator is the pattern of weakness – central facial paralysis typically spares the forehead due to bilateral innervation of forehead muscles.
Your doctor will gather important historical information, including:
- When you first noticed symptoms
- How quickly does paralysis develop
- Whether you have any muscle control in the affected areas
- Associated symptoms like hearing loss or tinnitus
Several specialised clinical tests may be performed, including the blink test (corneal reflex), Schirmer test (assessing lacrimation), stapedial reflex test, and taste tests. These evaluations help pinpoint the location of nerve damage within the facial nerve pathway.
Imaging and nerve conduction tests
Following the initial assessment, your physician may order additional diagnostic tests. Although imaging studies aren’t typically indicated in early evaluation of Bell’s palsy, they become necessary with certain warning signs – parotid mass, facial twitching, or additional neurologic symptoms.
MRI scanning proves particularly valuable for examining the entire facial nerve pathway. It can identify swelling, compression, or growths affecting the nerve, and is especially useful for imaging the cerebellopontine angle. Within the first month of paralysis onset, MRI with gadolinium contrast may show abnormal enhancement of various nerve segments.
CT scans are primarily recommended if complications from middle ear infection, necrotising otitis externa, head trauma, or malignancy are suspected.
Nerve conduction studies offer an objective assessment of nerve function and integrity. These include:
- Electroneurography (ENoG): Measures compound muscle action potential (CMAP) by stimulating the facial nerve at the stylomastoid foramen. Ideally performed within 14 days of onset, it helps determine the percentage of nerve degeneration by comparing affected and unaffected sides.
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluates electrical impulses along nerves and muscle tissue, helping assess weakness or paralysis in facial muscles. Unlike ENoG, EMG becomes most helpful 2-3 weeks after palsy onset and loss of nerve excitability.
The amplitude loss percentage calculated from nerve conduction studies provides valuable prognostic information. An abnormal facial nerve ultrasound has a negative predictive value of 77% for poor recovery (House-Brackmann Grade II or worse at 3 months).
Grading the severity of facial nerve paralysis
Once diagnosed, physicians use standardised scales to quantify the degree of facial paralysis. The House-Brackmann scale, approved by the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, serves as the reference standard. This six-point scale grades facial function from normal (Grade I) to complete paralysis (Grade VI).
The House-Brackmann classification evaluates both function at rest and with effort, making it comprehensive yet simple enough for clinical settings. Nevertheless, it has limitations in sensitivity for recording clinically significant changes.
For a more detailed assessment, the Sunnybrook facial grading system offers advantages. It evaluates facial symmetry at rest, voluntary movements, and synkinesis using a 0-100 scale (where 100 represents normal function). Physiotherapists often prefer this system for its sensitivity and specific assessment of synkinesis.
Other systems include the Sydney facial grading system, which assesses facial actions based on individual branches of the facial nerve. These standardised assessments provide objective measures for tracking progress throughout your physiotherapy journey.
Need a clear diagnosis and a path forward? Our Best Physio Clinic in Mohali uses advanced assessments to create your personalised treatment plan. Visit Our Clinic Page to Learn More.
Step 3: Starting Physiotherapy – What to Expect
Beginning physiotherapy for facial palsy involves several important steps designed to assess your condition, establish appropriate goals, and create an effective treatment plan. Understanding what to expect can help ease anxiety as you start this crucial rehabilitation journey.
First session: what happens
The initial physiotherapy session primarily focuses on a comprehensive assessment. Your therapist will gather detailed information about your symptoms, any recovery progress you’ve noticed, and other relevant medical history. This thorough evaluation helps determine the most effective treatment approach for your specific condition.
During this assessment, your therapist may use various techniques to evaluate your facial nerve function:
- Surface electromyography (sEMG) – Painless sticky electrodes placed on your face measure electrical activity in various muscles when you’re still and when attempting movements like raising your eyebrows, closing your eyes, smiling, or whistling
- Facial movement evaluation – The therapist examines muscle tone, normal movements, and any abnormal movements
- Muscle condition assessment – Noting whether facial muscles are weak and floppy or short and tight
- Eye health examination – Particularly important, as your therapist will provide advice about protecting your eyes from damage
At the end of the assessment, your therapist might recommend additional investigations if necessary, communicating with your referring doctor about further procedures.
Setting goals with your therapist
After completing the assessment, your therapist will help you understand how your facial nerve has been affected and the recovery process ahead. This educational component is crucial, as you’ll need to become intimately familiar with your face’s movements, appearance, and functions.
Your physiotherapist will classify your condition into specific treatment categories that guide goal-setting:
- Initiation
- Facilitation
- Movement control
- Relaxation
Together, you’ll establish realistic goals based on standardised assessment tools like the Facial Grading System (FGS), Facial Disability Index (FDI), House–Brackmann Scale, or Photoshop method. These tools help determine specific treatment objectives tailored to your symptoms.
Your therapist will undeniably emphasise understanding your facial motor dysfunction, teaching you to recognise desired movement patterns versus those to avoid. This awareness, especially when combined with biofeedback techniques, can minimise your risk of developing facial palsy complications.
Creating a personalised treatment plan
Based on your assessment results, the physiotherapist will develop a customised treatment plan addressing your specific needs. This plan typically includes a combination of approaches:
Core components often include:
- Active-assisted exercises with small, controlled movements
- Massage and stretching techniques to improve blood flow
- Facial retraining therapy to strengthen muscles and teach proper function
- Educational components about recovery processes and warning signs
For acute facial palsy (within the first 72 hours to 2 weeks), a multimodal approach involving a multidisciplinary team offers optimal results. Meanwhile, in the first 5 months after onset, your treatment plan will prioritise eye care to prevent corneal damage.
Your physiotherapist will explain that the quality of exercise performance matters more than quantity. Understanding this principle helps prevent abnormal movement patterns like synkinesis, which can develop if exercises aren’t performed correctly. Unlike other body muscles, facial muscles lack intrinsic feedback information, making precise, gentle rehabilitation through neuroplasticity essential.
Throughout your therapy journey, your physiotherapist will use photos, videos, and specialised software to track and visualise your progress. Most exercises should be performed in short sessions, typically three to four times daily, with up to 30 repetitions per exercise. Following your therapist’s recommendations for home practice is vital—repeating exercises several times daily gives facial muscles the best chance to relearn natural movements.
Uncertain about what physiotherapy entails? Let our expert team at the Best Physiotherapist Clinic in Mohali guide you through every step with compassion and expertise. Book your first session now!
Step 4: Core Exercises for Facial Muscle Recovery
Core exercises form the foundation of physiotherapy in facial palsy, directly targeting muscle weakness and coordination to restore function and appearance. These specialised techniques help activate muscles, promote circulation, and stimulate nerve regeneration while preventing unwanted complications.
Facial palsy exercises for symmetry
Rebuilding facial symmetry requires precise, controlled movements performed consistently over time. Essentially, these exercises help maintain muscle tone, reduce stiffness, improve mobility, prevent facial contractures, and develop better muscle control.
I recommend performing facial exercises 3-4 times daily in short sessions, with up to 30 repetitions per exercise. Accordingly, it’s best to:
- Sit in front of a mirror to monitor your movements
- Perform movements slowly and carefully
- Use your fingers to gently assist affected muscles when needed
- Stop immediately if you experience pain or discomfort
For optimal results, focus on specific muscle groups. Eyebrow exercises target the frontalis muscle, crucial for emotional expression. Eye exercises strengthen the orbicularis oculi muscle responsible for blinking. Nose exercises work the nasalis muscle, while lip and cheek exercises improve control of eating and speaking functions.
Stretching & strengthening routines
An effective strengthening routine should progress gradually as your control improves. Start with basic movements:
- Forehead workout: Gently lift your eyebrows while keeping your eyes open
- Eye control: Practice closing your eyelids tightly, creating wrinkles at the outer corners
- Nose exercises: Inhale deeply and sniffle, then wrinkle your nose and flare your nostrils
- Mouth control: Slowly pucker your lips together and push them forward
Throughout these exercises, use your fingers to prevent unwanted movement patterns or synkinesis, which could develop if exercises aren’t performed correctly.
Mirror therapy for coordination
Mirror therapy has emerged as a valuable technique for facial palsy rehabilitation. This approach uses visual feedback to stimulate different brain regions for movement, sensation, and pain.
During mirror therapy, you’ll perform facial neuromuscular retraining while observing your movements in a mirror. This creates visual stimulation to the brain, sending signals to move facial muscles repeatedly and preventing potential muscle contractures.
Research demonstrates mirror therapy’s effectiveness—patients receiving mirror therapy alongside standard rehabilitation showed significantly better results in House-Brackmann scores and quality of life compared to those receiving only traditional rehabilitation. One study found mirror therapy particularly helpful for improving face symmetry and decreasing synkinesis in the long term, with a quantifiable impact one year after onset.
EMG biofeedback in facial palsy
Electromyography (EMG) biofeedback provides an objective measurement of muscle activity, offering advantages over visual feedback alone. This technique uses surface electrodes placed on facial muscles to measure electrical activity during both rest and movement.
The biofeedback training typically spans two weeks, based on elements combined with Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy principles. Patients learn to perform facial movements more symmetrically while avoiding overly strong movements on the unaffected side and controlling unintended co-movements (synkinesis).
In a structured program, two bipolar foam hydrogel electrodes are attached to each side of the face, recording muscle activity in the cheek and mouth region. These electrodes connect to a biofeedback system that visualises muscle activity through feedback bars proportional to the activation level.
Studies show that biofeedback training leads to decreased overall muscle activity on both the synkinetic side and the contralateral side, demonstrating its effectiveness in facial muscle rehabilitation.
Struggling with facial symmetry? Our Physiotherapist in Mohali uses evidence-based techniques like mirror therapy and EMG biofeedback for effective recovery. Discover the difference expert care makes.
Step 5: Advanced Techniques for Better Results
Advanced rehabilitation techniques expand your facial palsy recovery options beyond basic exercises, often accelerating progress and addressing stubborn movement problems. These specialised approaches help patients who need additional intervention to achieve optimal facial function.
Neuromuscular re-education strategies
Neuromuscular facial re-education represents a sophisticated approach to facial rehabilitation that focuses on relearning movement patterns through specific feedback mechanisms. The process aims to facilitate proper muscle activity while suppressing abnormal movements that interfere with facial function.
This technique addresses a fundamental challenge in facial rehabilitation—facial muscles lack intrinsic feedback information (no internal sensory receptors), making it difficult to perform voluntary movements without external guidance. By providing visual feedback through mirrors or EMG biofeedback, your therapist helps you modify muscle activity by:
- Increasing activation in muscles that should move but don’t
- Decreasing activation in muscles that shouldn’t move but do
The approach relies heavily on neuroplasticity—your brain’s ability to reorganise itself by forming new neural connections. A 2011 study published in Neurology found that patients undergoing facial neuromuscular retraining experienced significantly better functional improvement than those who didn’t receive this intervention.
Electrical stimulation therapy
Electrical stimulation therapy remains one of the most debated advanced techniques in facial palsy rehabilitation. This approach delivers controlled electrical currents to promote nerve regeneration and preserve muscle mass during recovery.
Regarding effectiveness, results from animal studies appear promising—electrical stimulation reduced recovery time of the eye blink reflex by approximately 26% in one study. Remarkably, even a single session of stimulation proved as effective as multiple treatments for accelerating recovery.
Despite these encouraging findings, the clinical application remains contentious. Some clinicians assert that electrical stimulation improves recovery, yet others worry about potential adverse effects and increased synkinesis risk. Current research suggests electrical stimulation may be most beneficial for:
- Preventing muscle atrophy in denervated muscles
- Improving electrophysiological outcomes
- Reducing recovery time by approximately 30-50%
For optimal results, different current parameters are required for innervated versus denervated muscles—pulse durations of 100-300 microseconds for innervated muscles compared to at least 10 milliseconds for denervated muscles.
Manual therapy and massage
Facial massage plays a critical role in maintaining tissue pliability throughout your recovery process. Regular massage helps keep your face supple as nerves regenerate, potentially reducing stiffness and other side effects.
A small-scale 2020 study published in Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice found targeted massage techniques significantly improved facial symmetry and muscle function in Bell’s palsy patients over 8 weeks. Typical techniques focus on:
- Lower facial muscles: Grasping the centre of the lips and moving them into different positions
- Circular movements to improve circulation
- Gentle stretching to maintain tissue elasticity
The basic principle behind massage therapy is improving blood circulation, reducing muscle tightness, and supporting nerve healing, particularly when combined with other physical therapy approaches.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) represents another advanced option primarily known for limb rehabilitation but increasingly applied to facial palsy recovery. This technique uses patterns of movement and stretching to improve muscle function and coordination.
The current evidence for PNF in facial palsy treatment is limited but promising. A study examining patients receiving PNF with steroids showed faster clinical recovery (mean recovery time 70 days) compared to those receiving steroids alone (mean recovery time 124 days).
Typically, PNF is combined with other interventions rather than used alone. Studies have investigated PNF together with:
- Medications (antivirals and corticosteroids)
- Conventional treatment, including galvanic current stimulation
- Nerve stimulation
Assessment tools like the House-Brackmann Scale, Synkinesis Assessment Questionnaire, and Facial Disability Index are commonly used to measure progress with PNF treatment.
Plateaued in your recovery? Explore advanced neuromuscular re-education and other techniques with the Best Physiotherapist in Mohali at The Brigit Clinic. Call 📞 0172 - 3137922 to Advance Your Treatment.
Step 6: Supporting Daily Function and Expression
Beyond mastering exercises and advanced techniques, physiotherapy in facial palsy must address daily functional challenges that significantly impact quality of life. Nearly one-third (29%) of patients experience permanent facial function deficits affecting critical activities, creating obstacles that specialised rehabilitation strategies can help overcome.
Speech improvement through physiotherapy
Facial paralysis often compromises speech clarity, especially for sounds requiring lip seal such as ‘b’, ‘p’, ‘m’, ‘v’, and ‘f’ consonants. Studies reveal that patients with unilateral facial palsy demonstrate significantly poorer articulation compared to healthy individuals.
Interestingly, the relationship between palsy severity and speech impacts isn’t straightforward—research indicates no direct correlation between the degree of facial palsy and its effect on communication. This underscores why individualised assessment by a speech-language therapist or physiotherapist with facial rehabilitation expertise remains vital.
Speech therapy typically incorporates:
- Specific articulation exercises focusing on problematic consonants
- Compensatory strategies to maximise intelligibility
- Combined approaches with facial exercises to strengthen relevant muscles
Eating & drinking function recovery
Facial weakness creates substantial challenges during meals. The inability to form a proper lip seal makes containing food and fluids difficult, while weakened cheek muscles allow food to collect on the affected side. These complications often lead patients to avoid eating in social settings.
For improved eating and drinking, consider these practical techniques:
First, support your lower lip with transpore tape (2.5 cm width) positioned to lift toward the outer mouth corner. Cheek taping can likewise provide structural support during the flaccid recovery stage. Additionally, specialised tools like Kapi-cups—thin plastic mugs with cutouts allowing drinking without head-tipping—can dramatically improve fluid intake.
Dietary modifications prove equally important—choosing softer foods, avoiding mixed consistencies (like cereal in milk), and taking smaller bites all contribute to better mealtime experiences.
Eye protection & blinking recovery
Facial nerve paralysis frequently affects tear production and blinking ability, creating a serious risk for corneal damage. Eye protection represents the highest priority during early recovery (first 5 months).
Common eye protection approaches include:
- Artificial tears are applied hourly to maintain moisture
- Eye ointments for inflammation and soreness
- Medical tape or eye patches to prevent drying from air conditioning or fans
For long-term blinking issues, eyelid weights offer a more permanent solution. Made from gold or platinum and implanted into the upper eyelid, these weights help restore proper blinking function. This procedure requires careful planning and precise implementation by facial plastic and oculoplastic surgeons.
Improvement in facial expressions
Facial expressions constitute the foundation of non-verbal communication, with their absence profoundly affecting social interactions. Patients living with incomplete recovery frequently experience psychological distress, depression, and social alienation.
Physiotherapy focuses on restoring expressiveness through neuromuscular retraining techniques using a mirror or EMG biofeedback. As recovery progresses, patients learn to refine control of specific muscle groups responsible for different expressions, gradually rebuilding their non-verbal communication repertoire.
Throughout rehabilitation, remember that improvement varies by individual. Seeking qualified professional guidance ensures you receive appropriate, personalised interventions tailored to your specific functional needs.
Difficulty with speech, eating, or eye closure? We specialise in restoring daily function. Find supportive and effective Physiotherapy in Mohali at our state-of-the-art clinic. Let us help you regain confidence.
Step 7: Home Care and Long-Term Maintenance
Successful facial palsy rehabilitation requires consistent practice at home, long after your supervised therapy sessions end. The daily exercises and self-care routines you perform become fundamental to your long-term recovery.
Daily home exercise routines
Home exercise programs should complement your professional therapy sessions. For optimal results, your therapist will typically prescribe:
- 3 to 5 specific exercises targeting your affected areas
- 5 to 10 repetitions of each exercise
- Practice sessions twice daily
Remember that quality matters more than quantity. Indeed, all movements should be very gentle and performed with extreme care. Forceful attempts with weakened muscles can lead to complications like synkinesis or unwanted facial movements. Only practice exercises at home after you can perform them accurately and recognise when you’re doing them incorrectly.
Massage for facial muscles at home
Facial massage plays a vital role alongside exercises in maintaining healthy, mobile muscles throughout recovery. After learning proper techniques from your therapist, you can perform regular massages to:
- Keep muscles supple and healthy
- Lengthen muscles that have become short or tight
- Improve circulation to support nerve healing
For optimal technique, use your palms and fingertips to massage the sides of your face in an upward motion. Throughout the process, use Vitamin E or jojoba oil to improve gliding motion without causing breakouts. Focus on sweeping motions rather than rubbing, as excessive rubbing may irritate skin and cause inflammation.
Tracking progress and setbacks
Keeping a photographic diary of your recovery provides objective evidence of improvement. As part of your monitoring:
- Take baseline photos as soon as possible after diagnosis
- Repeat photos every five days for the first three weeks
- Continue with photos every two weeks thereafter
This visual documentation helps both you and your healthcare providers assess progress objectively, as daily observation makes subtle changes difficult to notice.
When to revisit your therapist
Schedule a follow-up with your therapist if:
- You notice no recovery within three months
- New abnormal movements develop
- You experience increasing tightness or discomfort
- You’ve completed your home program but plateaued
Above all, remember that recovery often progresses slowly, hence patience remains essential. Many patients don’t see initial improvement for several months, yet therapy remains effective even when started years after onset.
Need a sustainable home exercise plan? Get a tailored routine from our Physio Clinic in Mohali to ensure you practice correctly and safely between sessions. Your long-term recovery is our priority.
Step 8: Measuring Success and Adjusting Treatment
Tracking progress objectively forms the cornerstone of effective facial palsy rehabilitation, allowing both patient and therapist to make informed decisions about treatment adjustments.
Using outcome measures like FDI and Sunnybrook
Measuring facial palsy improvement requires standardised assessment tools. The House-Brackmann Scale (HBS) remains the most commonly used method for recording functional recovery, appearing in numerous studies. The Sunnybrook Facial Grading System offers greater sensitivity by evaluating resting symmetry, movement symmetry, and synkinesis on a 0-100 scale. Notably, physiotherapists often prefer this system specifically for its detailed assessment of synkinesis.
Patient-reported outcomes provide equally vital information. The Facial Disability Index (FDI) measures both physical function (FDIP) and social/well-being elements (FDIS). These scores help quantify quality of life impacts that clinical grades might miss.
Recovery of facial symmetry over time
Facial symmetry typically improves gradually with appropriate physiotherapy. Patients using mirror book therapy show approximately 25% increase in Facial Grading System scores, 21.6% improvement in FDIP, and 24.5% increase in FDIS. Voluntary movement scores specifically demonstrate significant increases between the 6th and 12th months of treatment.
Adapting therapy for chronic cases
Remarkably, facial rehabilitation benefits patients regardless of age, gender, or when treatment begins. For chronic cases, treatment modifications based on regular reassessment become essential. Surface-based measurement techniques can detect subtle symmetry improvements, guiding therapy adjustments even in long-standing cases. As treatment progresses, outcome measures help identify plateaus requiring fresh therapeutic approaches.
Want to accurately track your recovery? Our Physio Clinic Near Me in Mohali uses standardised tools like the Sunnybrook scale to measure success and adjust your plan for the best outcomes. Get a Progress Evaluation Today.
Conclusion
Facial palsy rehabilitation represents a journey rather than a quick fix. Though each person’s path to recovery differs, physiotherapy undoubtedly plays a crucial role in restoring both function and confidence. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored everything from recognising symptoms to implementing advanced rehabilitation techniques.
Patience remains essential during recovery. Most patients see significant improvement within 3-6 months, but complete rehabilitation might take longer, especially for the 30% who don’t recover spontaneously. Your commitment to consistent practice makes all the difference in your outcome.
Actually, physiotherapy for facial palsy works best as a comprehensive approach. Combining core exercises, neuromuscular re-education, and specialised techniques like mirror therapy or EMG biofeedback maximises your chances of regaining facial symmetry and function. These evidence-based approaches help reestablish neural pathways and muscle coordination through neuroplasticity.
Beyond physical recovery, physiotherapy addresses psychological aspects of facial palsy. Many patients experience social anxiety and depression due to changes in appearance and function. Consequently, rehabilitation must target both physical restoration and emotional well-being.
Remember that support exists regardless of when your facial palsy began. Research shows benefits from therapy even years after onset, so previous disappointments needn’t determine your future progress. Your physiotherapist can adjust your treatment plan as needed based on objective measurements and your personal goals.
Facial palsy might temporarily change how you interact with the world, but with proper physiotherapy, dedication to home exercises, and professional guidance, you can achieve significant functional improvement and regain your confidence. This step-by-step approach provides the roadmap—now your journey toward recovery can begin.
Key Takeaways
This comprehensive guide reveals evidence-based strategies for facial palsy recovery that can significantly improve outcomes when applied systematically.
• Early intervention matters most: Seek medical attention within 72 hours of symptom onset – patients receiving early steroid treatment achieve 83% full recovery versus only 72% without treatment.
• Quality over quantity in exercises: Perform facial exercises 3-4 times daily with gentle, controlled movements – forceful attempts can cause complications like synkinesis and unwanted facial movements.
• Mirror therapy accelerates recovery: Visual feedback through mirror exercises stimulates brain regions for movement and significantly improves facial symmetry while reducing long-term complications.
• Home practice determines success: Consistent daily exercise routines and facial massage maintain muscle health and support nerve healing throughout the recovery process.
• Recovery takes patience but works: While 70% recover naturally within 3-6 months, physiotherapy benefits patients regardless of age or when treatment begins – even years after onset.
The key to successful facial palsy rehabilitation lies in combining professional guidance with dedicated home practice, using evidence-based techniques that address both physical function and emotional well-being for comprehensive recovery.
FAQs
Q1. How long does it typically take to recover from facial palsy with physiotherapy?
A1. Recovery time varies, but most patients see significant improvement within 3-6 months of starting physiotherapy. Complete rehabilitation may take longer, especially for the 30% who don’t recover spontaneously. Consistent practice and patience are key to achieving the best outcomes.
Q2. What are some core exercises for facial muscle recovery?
A2. Core exercises include gentle movements targeting specific muscle groups, such as lifting eyebrows, closing eyes tightly, wrinkling the nose, and puckering lips. These should be performed 3-4 times daily in short sessions, with up to 30 repetitions per exercise, while monitoring in a mirror to ensure proper technique.
Q3. Can physiotherapy help with speech and eating difficulties caused by facial palsy?
A3. Yes, physiotherapy can significantly improve speech clarity and eating function. Techniques include specific articulation exercises, compensatory strategies for intelligibility, and methods to support lip seal and cheek muscles during meals. Specialised tools and dietary modifications may also be recommended.
Q4. Is electrical stimulation effective in facial palsy treatment?
A4. The effectiveness of electrical stimulation in facial palsy treatment is debated. Some studies suggest it can reduce recovery time by 30-50% and help prevent muscle atrophy. However, its clinical application remains controversial due to potential risks of adverse effects and increased synkinesis.
Q5. How can I track my progress during facial palsy rehabilitation?
A5. Progress can be tracked through standardised assessment tools like the House-Brackmann Scale and Sunnybrook Facial Grading System. Additionally, keeping a photographic diary with regular photos every few weeks provides visual evidence of improvement. Patient-reported outcome measures like the Facial Disability Index also help quantify quality of life impacts.
About Dr. Aayushi – Best Physiotherapist in Mohali
Dr. Aayushi is a highly skilled and compassionate physiotherapist dedicated to helping patients overcome the challenges of facial palsy. With specialised training in neurological rehabilitation and a deep understanding of facial neuromuscular retraining, she is recognised as a leading Physiotherapist in Mohali. At The Brigit Clinic, Dr. Aayushi combines evidence-based techniques, such as mirror therapy and EMG biofeedback, with a personalised touch to create effective treatment plans that restore both function and confidence. Her patient-centric approach ensures that every individual receives the dedicated care and support they need throughout their recovery journey, making her the preferred choice for anyone seeking the Best Physiotherapist in Mohali.
Book an Appointment today -
📞 0172 - 3137922 | 🌐 Read Reviews | 📍 Get Directions